Morning
Collagen
Collagen is a key component in bones, skin, muscles, and other body parts. It may help improve skin health, relieve joint pain, and prevent bone loss, among other things.
Collagen supplementation provides a variety of health benefits.
- May improve skin health
- May relieve joint pain
- May prevent bone loss
- May boost muscle mass
- May promote heart health
- Other health benefits
Collagen supplements have several benefits related to skin, joint, bone, muscle, and heart health. There’s scant evidence to support collagen’s purported effects on weight loss or gut or brain health.
probiotics, multivitamins
Source: (https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/collagen-benefits#side-effects)

Probiotics
Probiotics are live microorganisms that can be consumed through fermented foods or supplements .
More and more studies show that the balance or imbalance of bacteria in your digestive system is linked to overall health and disease.
- Probiotics help balance the friendly bacteria in your digestive system
- Probiotics can help prevent and treat diarrhea
- Probiotic supplements improve some mental health conditions
- Certain probiotic strains can help keep your heart healthy
- Probiotics may reduce the severity of certain allergies and eczema
- Probiotics can help reduce symptoms of certain digestive disorders
- Probiotics may help boost your immune system
- Probiotics may help you lose weight and belly fat
Source : (https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/8-health-benefits-of-probiotics#how-to-benefit)

Multivitamins
Vitamins and minerals are substances your body needs to survive, grow, and work the way it should. Different vitamins and minerals have different jobs, affecting everything from your nerves and bones to how well your blood clots.
Eating a balanced diet with plenty of vegetables, fruits, and whole grains should provide the vitamins and minerals you need. But if you can’t always eat healthy meals, taking supplements might help.
About one-third of American adults take daily supplements containing multiple vitamins and minerals. These are commonly known as multivitamins.
Source: (https://www.webmd.com/diet/health-benefits-of-multivitamins)
Lunch
Omega-3 fatty acids
Omega-3 fatty acids have many potential benefits for your cardiovascular health. One key benefit is that they help lower your triglyceride levels. Too many triglycerides in your blood (hypertriglyceridemia) raises your risk of atherosclerosis, and through this, can increase your risk of heart disease and stroke. So, it’s important to keep triglyceride levels under control. In addition, omega-3s may help you by raising your HDL (good) cholesterol and lowering your blood pressure.
Some studies show omega-3s may lower your risk for:
- Cardiovascular disease (CVD).
- Death, if you have CVD.
- Sudden death caused by an abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia).
- Blood clots.
- Beyond heart health, omega-3s may help lower your risk of developing:
- Some forms of cancer, including breast cancer.
- Alzheimer’s disease and dementia.
- Age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
Research continues to investigate these and other possible benefits.
Source: (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/17290-omega-3-fatty-acids)

Calcium
Your body needs calcium to build and maintain strong bones. Your heart, muscles and nerves also need calcium to function properly.
Some studies suggest that calcium, along with vitamin D, may have benefits beyond bone health: perhaps protecting against cancer, diabetes and high blood pressure. But evidence about such health benefits is not definitive.
Source: (https://www.mayoclinic.org)

AFTERNOON
Vitamin C
7 Impressive Ways Vitamin C Benefits Your Body
Vitamin C has many health benefits. For example, it helps strengthen our immune system and may help lower blood pressure. It is found in many fruits and vegetables.
Vitamin C is an essential vitamin, meaning your body can’t produce it. Yet, it has many roles and has been linked to impressive health benefits.
It’s water-soluble and found in many fruits and vegetables, including oranges, strawberries, kiwi fruit, bell peppers, broccoli, kale, and spinach.
Here are 7 scientifically proven benefits of taking a vitamin C supplement.
- May reduce your risk of chronic disease
Vitamin C is a strong antioxidant that can boost your blood antioxidant levels. This may help reduce the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease.
- May help manage high blood pressure
Vitamin C supplements have been found to lower blood pressure in both healthy adults and those with high blood pressure.
- May lower your risk of heart disease
Vitamin C supplements have been linked to a reduced risk of heart disease. These supplements may lower heart disease risk factors, including high blood levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol and triglycerides.
- May reduce blood uric acid levels and help prevent gout attacks
Vitamin-C-rich foods and supplements have been linked to reduced blood uric acid levels and lower risk of gout.
- Helps prevent iron deficiency
Vitamin C can improve the absorption of iron that is poorly absorbed, such as iron from meat-free sources. It may also reduce the risk of iron deficiency.
- Boosts immunity
Vitamin C may boost immunity by helping white blood cells function more effectively, strengthening your skin’s defense system, and helping wounds heal faster.
- Protects your memory and thinking as you age
Low vitamin C levels have been linked to an increased risk of memory and thinking disorders like dementia, while a high intake of vitamin C from foods and supplements has been shown to have a protective effect.
Source: (https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/vitamin-c-benefits)

B vitamins
B vitamins play a vital role in maintaining good health and well-being. As the building blocks of a healthy body, B vitamins have a direct impact on your energy levels, brain function, and cell metabolism.
Vitamin B complex may help prevent infections and help support or promote:
- Cell health
- Growth of red blood cells
- Energy levels
- Eyesight
- Brain function
- Digestion
- Appetite
- Proper nerve function
- Hormones and cholesterol production
- Cardiovascular health
- Muscle tone
Source : (https://www.healthline.com/health/food-nutrition/vitamin-b-complex#benefits)

EVENING
Magnesium
12 Evidence-Based Health Benefits of Magnesium
- Involved in hundreds of biochemical reactions in your body
- Energy creation: converting food into energy
- Protein formation: creating new proteins from amino acids
- Gene maintenance: helping create and repair DNA and RNA
- Muscle movements: aiding in muscle contraction and relaxation
- Nervous system regulation: regulating neurotransmitters, which send messages throughout your brain and nervous system
- May boost exercise performance
You may need more magnesium during exercise than when you’re resting, depending on the activity. Magnesium helps move blood sugar into your muscles and dispose of lactate, which can build up during exercise and cause fatigue. Studies show magnesium supplements may be particularly beneficial for improving exercise performance in older adults and those with a deficiency in this nutrient.
- May combat depression
Magnesium plays a critical role in brain function and mood; low levels are linked to an increased risk of depression. A 2020 review suggested that stress may deplete magnesium, increasing susceptibility to stress and depression. What’s more, supplementing with this mineral may help reduce symptoms of depression.
- May support healthy blood sugar levels
Magnesium supplements may improve blood sugar levels, insulin sensitivity, and other risk factors for type 2 diabetes.
- May promote heart health
Magnesium plays an important role in keeping your heart healthy and strong. Magnesium may help lower blood pressure levels and reduce several risk factors for heart disease. Still, more research is needed.
- Boasts anti-inflammatory benefits
Low magnesium intake is linked to increased levels of inflammation, which plays a crucial role in aging and chronic disease. Magnesium has been shown to help fight inflammation by reducing markers such as CRP and interleukin-6.
- May help prevent migraine attacks
Migraine headaches can be painful and often cause nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and noise. Some researchers believe that people with migraine are more likely than others to have a magnesium deficiency. People with migraine may have low magnesium levels. Some studies show that supplementing with this mineral may provide relief from migraine attacks.
- May improve PMS symptoms
Premenstrual syndrome (PMS) is one of the most common conditions in female-bodied people of childbearing age. It often causes symptoms such as water retention, abdominal cramps, tiredness, and irritability. Some research suggests that magnesium supplements help relieve PMS symptoms and other conditions such as menstrual cramps and migraine attacks. Some studies suggest that magnesium supplements help improve PMS symptoms, though more research is necessary.
- May promote bone health
Magnesium is crucial for maintaining bone health and protecting against bone loss. In fact, 50–60% of your body’s magnesium is found in your bones. Some studies associate lower levels of this mineral with a higher risk of osteoporosis, which causes bones to become brittle and weak. Magnesium is important for bone health. Some studies tie a higher intake to a lower risk of osteoporosis, fractures, and bone loss.
- May support better sleep
Magnesium supplements are often used as a natural remedy for sleep issues such as insomnia. This is because magnesium regulates several neurotransmitters involved in sleep, such as gamma aminobutyric acid. Increasing your intake of magnesium through foods or supplements may help treat certain sleep issues and improve sleep quality.
- May help reduce anxiety symptoms
Some research suggests that magnesium helps treat and prevent anxiety. One review concluded that magnesium supplements might help reduce mild to moderate anxiety but noted that research is conflicting — and that the effects of supplements haven’t been studied beyond 3 months. Magnesium may help reduce symptoms of anxiety and decrease stress, but more studies are needed.
- Safe and widely available
Magnesium is essential for many aspects of health. The recommended daily intake is 400–420 mg for males and 310–320 mg for females. You can get this mineral from both food and supplements.
Source: (https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/magnesium-benefits#heart-health)
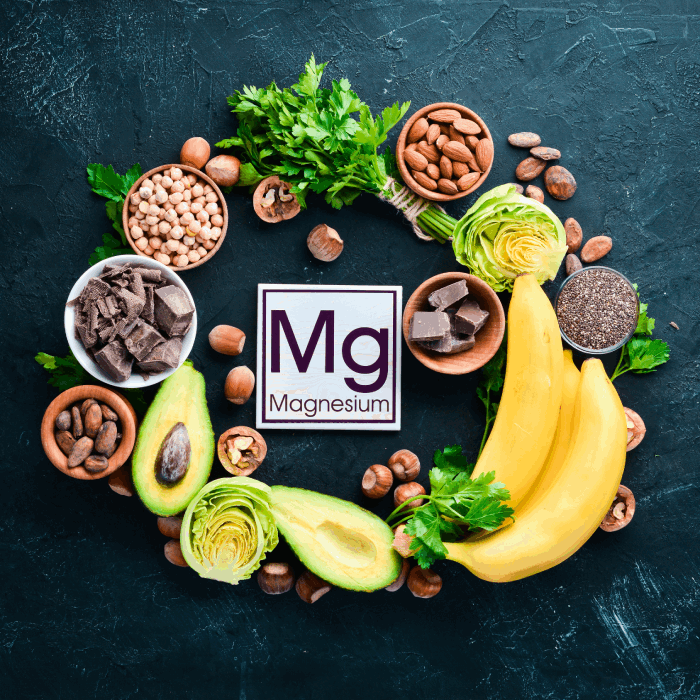
Melatonin
Melatonin is a hormone made in the body. It regulates night and day cycles or sleep-wake cycles. Melatonin in supplements is usually made in a lab.
Darkness triggers the body to make more melatonin, which signals the body to sleep. Light decreases melatonin production and signals the body to be awake. Some people who have trouble sleeping have low levels of melatonin. It’s thought that adding melatonin from supplements might help them sleep.
People most commonly use melatonin for insomnia and improving sleep in different conditions, such as jet lag. It is also used for depression, chronic pain, dementia, and many other conditions, but there is no good scientific evidence to support most of these uses. There is also no good evidence to support using melatonin for COVID-19.
Source: (https://www.webmd.com/vitamins/ai/ingredientmono-940/melatonin)

stylisphere
most read